Use the route planner to manually calculate and compare routes through a network.
When should I use this?
Use the route planner to:
- Inspect routing behaviour in a network
- Compare routes before and after network edits
- Understand the effect of direction changes, access restrictions, or speed limits
The route planner works on a network and does not require a scenario or datasets.
Before you start
- A project in the area you want to work in.
Steps
1. Open the route planner for a network
- Open your project
- Scroll to the Networks section
- Click Route planner next to the network you want to test
A map will open with the network and the route planner.
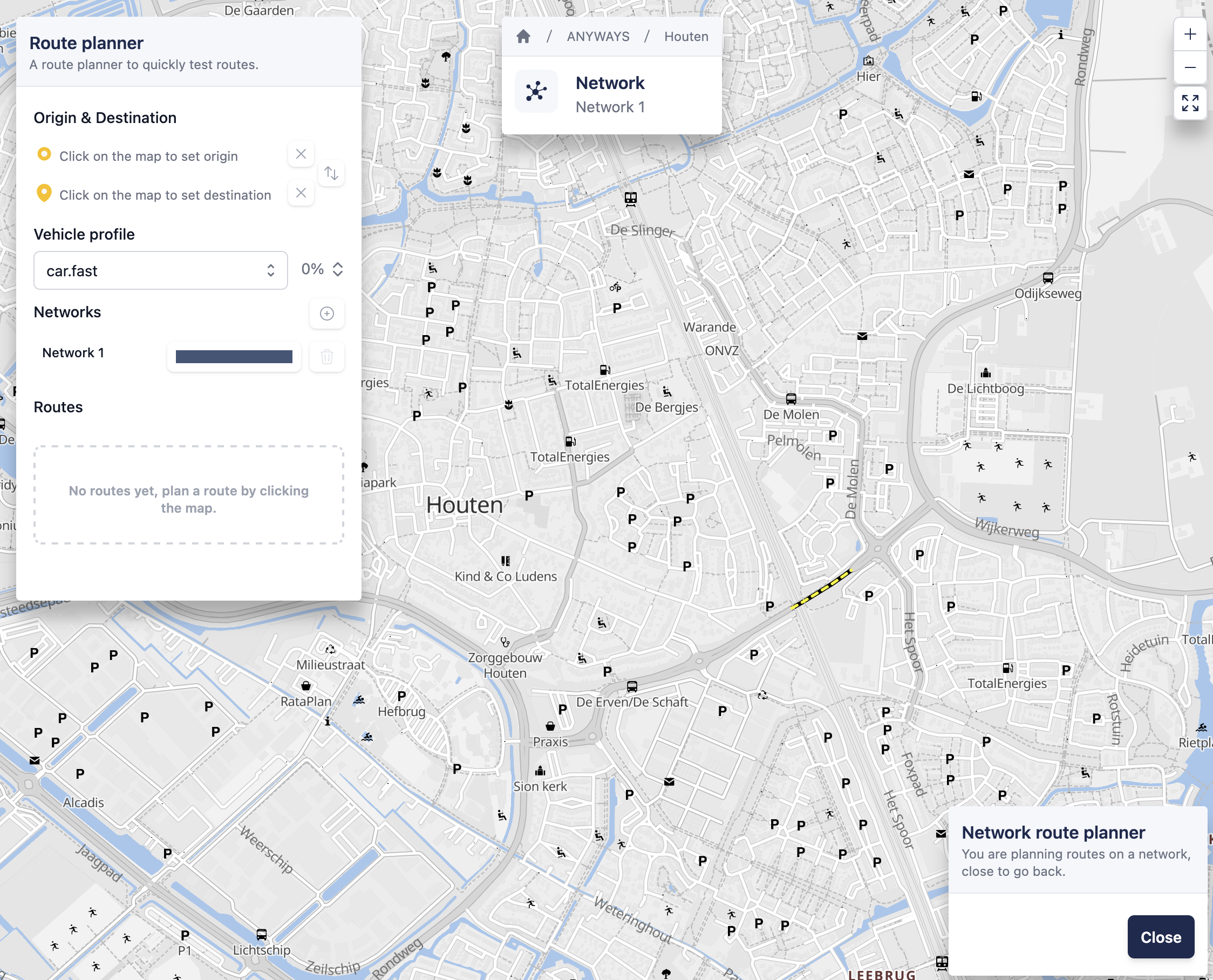
2. Choose origin and destination
- Click once on the map to set the origin
- Click a second time on the map to set the destination
The route planner will calculate a route between the two points.
3. Inspect the route
Once the route is calculated, you can:
- See the selected route on the map
- Review route length and travel time
- Adjust route planner options to compare different modes of travel
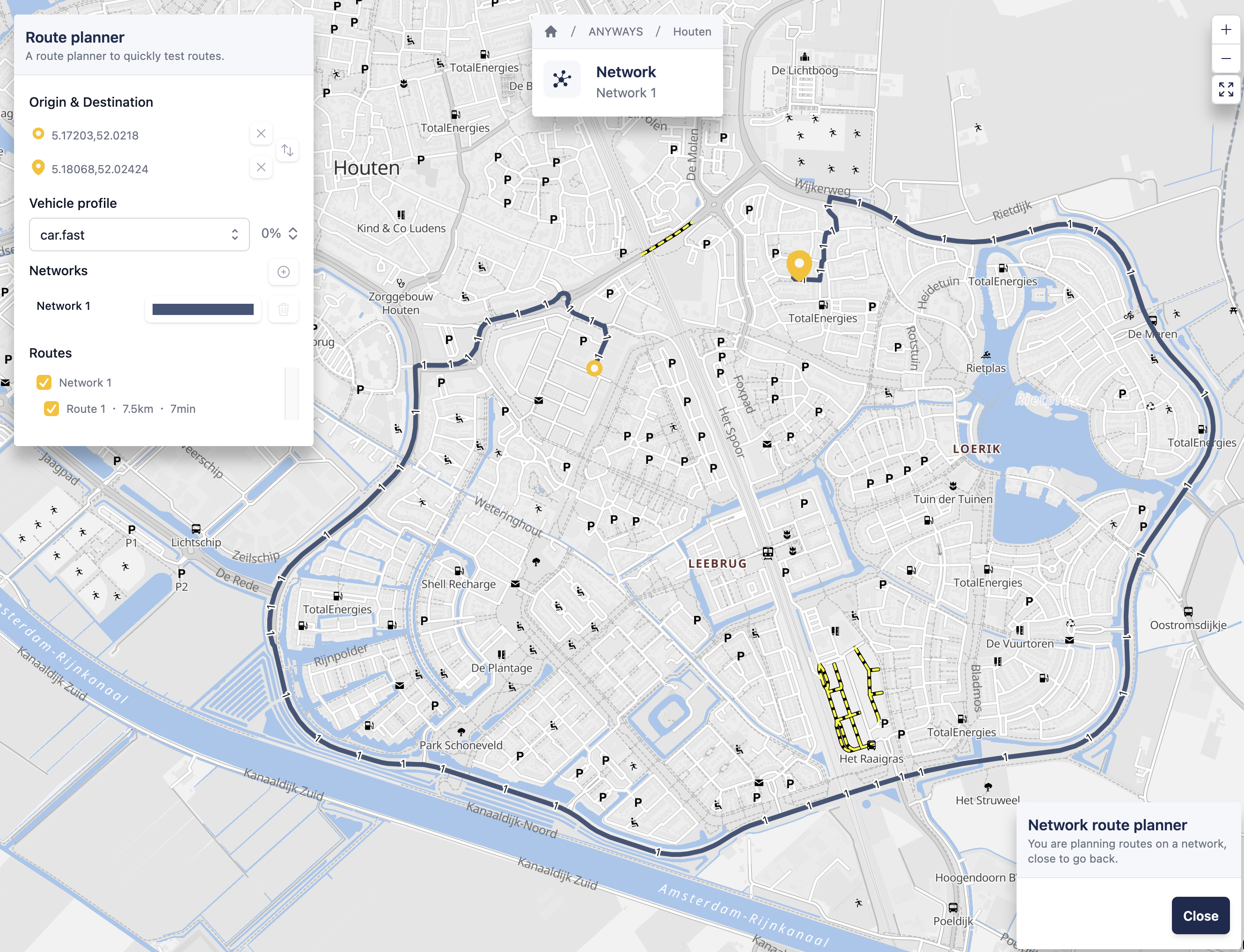
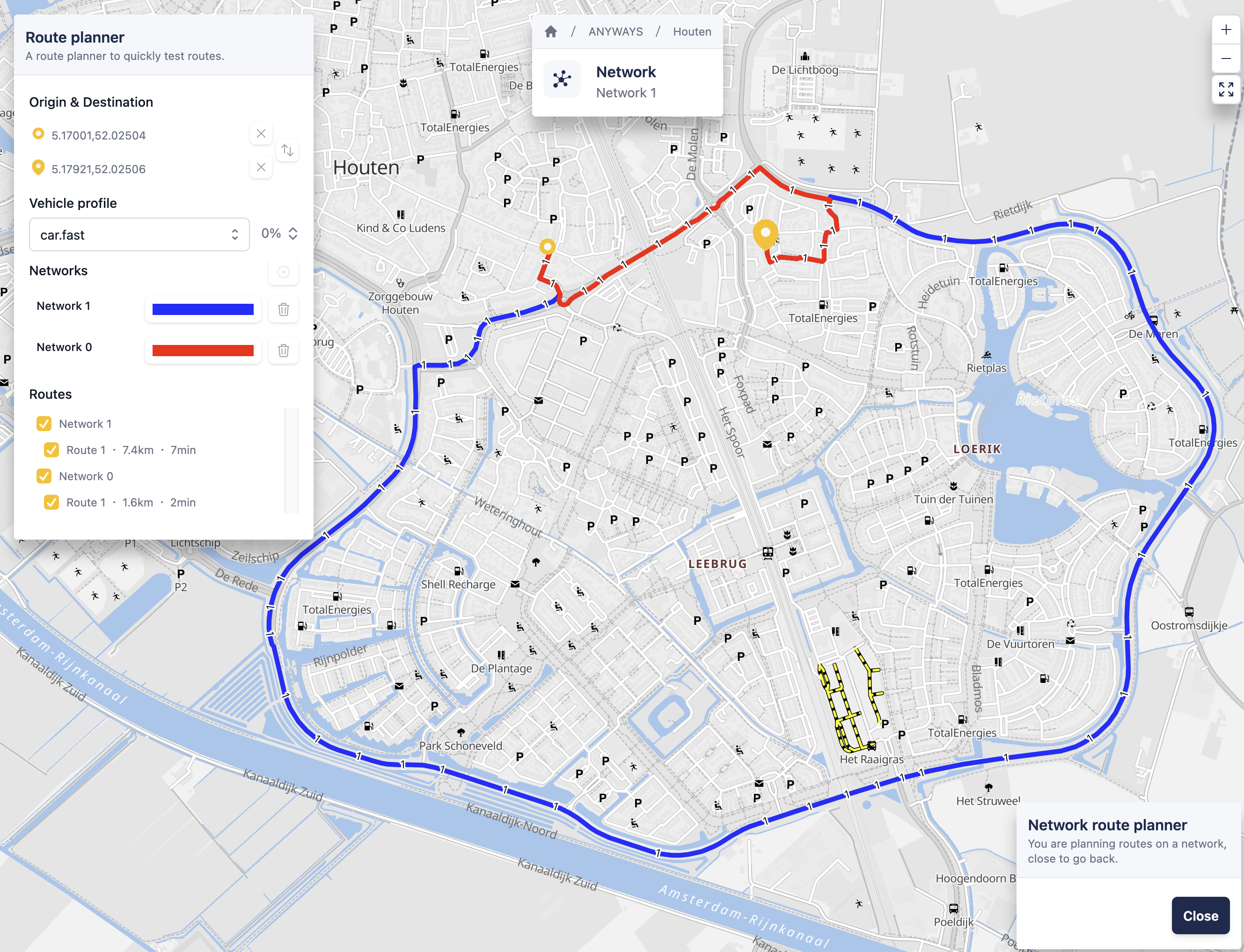
Compare routes across networks
You can compare routes between different networks, for example to see the effect of edits.
- In the route planner widget on the map, add another network. Click the + button to do this.
- The route planner will calculate the same origin–destination route for each selected network
- Compare the routes and travel times shown on the map
This is useful for:
- Comparing a base network with an edited network
- Evaluating the impact of specific changes
Relation to datasets
The route planner is used in two ways in ANYWAYS:
- Manually, to explore and compare routes
- Automatically, to assign routes when creating datasets